- /
- Article / What is Coefficient of Friction? Units, Types, and Formula Explained
What is Coefficient of Friction? Units, Types, and Formula Explained

You’ve probably noticed how some surfaces feel more slippery than others—like walking on ice versus walking on rough concrete. That difference is due to something called the coefficient of friction (COF). It is a small but important concept used widely in industries like packaging, automotive, construction, and material testing.
In this blog, we’ll break down what the coefficient of friction means, how it’s measured, the types, and why it matters in real-life applications.
What Do We Mean by Coefficient of Friction?
The coefficient of friction is a number that shows how much resistance one surface puts up when something slides over it. It is basically the grip between two surfaces. A higher number means more resistance—like rubber on a road. A lower number means less grip—like ice under your shoes.
This value is found using a simple formula:
μ = Friction Force / Normal Force
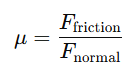
That’s just a fancy way of saying: how hard it is to move something divided by how hard it's being pressed down.
Coefficient of Friction Formula
The fundamental formula for calculating the coefficient of friction is:-
μ = Ff / Fn
Where:
- μ is the coefficient of friction
- Ff is the frictional force (in Newtons)
- Fn is the normal force (in Newtons)
This simple yet powerful equation helps determine how easily one object can slide over another.
Types of Coefficient of Friction
There are two main Types of coefficient of friction:
Static Coefficient of Friction (μs):
The Coefficient static friction represents the resistance to motion when the object is at rest. It defines how much force is needed to initiate movement. This is always higher than the kinetic friction.
Formula:
μs = Fs / Fn
Where Fs is the maximum force applied before motion begins.
Kinetic Coefficient of Friction (μk):
The Coefficient kinetic friction (also known as dynamic friction) applies when the object is already moving. It describes the force required to keep the object in motion.
Formula:
μk = Fk / Fn
Where Fk is the force required to maintain constant motion.
How to Find the Coefficient of Friction
To find the coefficient of friction, you need two things:-
- The frictional force
- The normal force
You can calculate both static and kinetic coefficients using these steps:
How to Calculate Coefficient of Static Friction
Gradually increase the force until the object just begins to slide. The maximum force before movement is static friction.
Formula:
μs = Fmax / Fn
Where:
- Fmax is the maximum applied force before sliding
- Fn is the normal force (typically mass × gravity)
How to Calculate Coefficient of Kinetic Friction
Once the object is in motion, apply enough force to keep it sliding at a constant speed.
Formula:
μk = Fk / Fn
Where Fk is the applied force required to keep the object moving.
Real World Application- Why Coefficient of Friction Testing Matters
In industries like packaging, automotive, plastics, textiles, and printing, friction can impact product quality, machine performance, and user experience. That is why accurate friction testing is critical.
For instance:
- Low friction in films might cause slippage during packaging.
- High friction may lead to material jamming in machines.
That’s where a Coefficient of Friction Tester becomes essential.
The Solution: Coefficient of Friction Tester
In quality-driven industries, manual testing for friction isn't always practical or accurate. That's where the Coefficient of Friction Tester becomes the ideal solution. This precision instrument automates the process of measuring both static (μs) and kinetic (μk) friction using standardized methods, reducing human error and improving reliability.

How It Works:
The tester includes a motorized sled that pulls a sample over a base substrate. As the sled begins to move, the machine records:
- Maximum force before movement begins → used to calculate μs
- Force required to maintain steady motion → used to calculate μk
The software automatically calculates:
- Static Coefficient of Friction (μs = Fmax / Fn)
- Kinetic Coefficient of Friction (μk = Fk / Fn)
Key Benefits:
- Fast and accurate readings
- Compliance with ASTM D1894, ISO 8295, TAPPI standards
- Suitable for plastic films, laminates, paper, foil, and coated surfaces
- Essential for R&D, production, and QC labs
Investing in a Coefficient of Friction Tester not only improves product performance but also ensures consistency and compliance with international quality benchmark.
Where is Coefficient of Friction Testing Used?
- Packaging Industry: To test plastic films, paperboard, and cartons
- Textile Industry: To measure inter-fabric friction
- Printing Industry: To ensure smooth feed-through in machines
- Automotive Sector: To test brake pads, tire treads, and seat materials
- Plastic & Polymer Industry: For slip characteristics in molding and converting
Typical Coefficient of Friction Values
| Material Pair | μs (Static) | μk (Kinetic) |
| Rubber on concrete (dry) | 1.0 | 0.8 |
| Wood on wood | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Steel on steel (dry) | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| Teflon on steel | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Paper on paper | 0.5 | 0.4 |
Note: Values vary depending on surface finish, lubrication, and environmental conditions.
FAQs
Q: What is the coefficient of friction?
It’s a dimensionless value (μ) that describes how much resistance one surface encounters when sliding over another. It can be static (μs) or kinetic (μk).
Q: What is the unit of coefficient of friction?
The coefficient of friction unit is unitless because it is a ratio of two forces (both measured in Newtons).
Q: How do you calculate the coefficient of friction?
Use the formula:
μ = Ff / Fn
Where Ff is the frictional force and Fn is the normal force.
Q: How to calculate coefficient of kinetic friction?
Once an object is in motion, measure the force needed to keep it moving and divide by the normal force:
μk = Fk / Fn
Q: How to calculate coefficient of static friction?
Measure the maximum force just before the object starts moving and divide it by the normal force:
μs = Fmax / Fn
Q: Why coefficient of friction important in packaging?
A: It helps determine how materials like plastic films or paperboard will behave during handling, stacking or transport. A suitable COF ensures product stability and reduces damage risk.
Q: How does a Co-efficient of Friction Tester work?
A: It measures the force required to move a sled over a test material under controlled conditions. It calculates both static and kinetic COF values using sensors and digital display units.
Q: What standards are followed for COF testing?
A: Common standards include ASTM D1894 and ISO 8295. These ensure consistency and accuracy in testing results.
Best Coefficient of Friction Tester Price in India
Looking for an accurate and affordable Coefficient of Friction Tester? Get the best deal now from Presto Group – trusted by top manufacturers.
Call: +91 9210 903 903
Email: info@prestogroup.com
Enquire now for the latest Coefficient of Friction Tester price and specifications!


