- /
- Blog / Advanced Optical Comparator – Profile Projector
Advanced Optical Comparator – Profile Projector

In the world of precision measurement and quality inspection, optical comparators, also known as profile projectors, play a pivotal role. These non-contact optical instruments project the magnified silhouette of a part onto a screen for accurate dimensional comparison against prescribed limits. From automotive to aerospace, and electronics to manufacturing, these tools are indispensable.
This blog delves deep into the profile projector working principle, its types (vertical and horizontal), advantages and disadvantages, real-world applications of profile projector, and even sheds light on profile projector specifications, pricing, and more.
What is an Optical Comparator or Profile Projector?
A profile projector (also known as an optical comparator) is an optical instrument that magnifies the outline of a part and projects it on a screen for measurement and comparison against standards. It allows users to inspect minute components, holes, curves, and threads without physically touching the part, thus avoiding deformation.
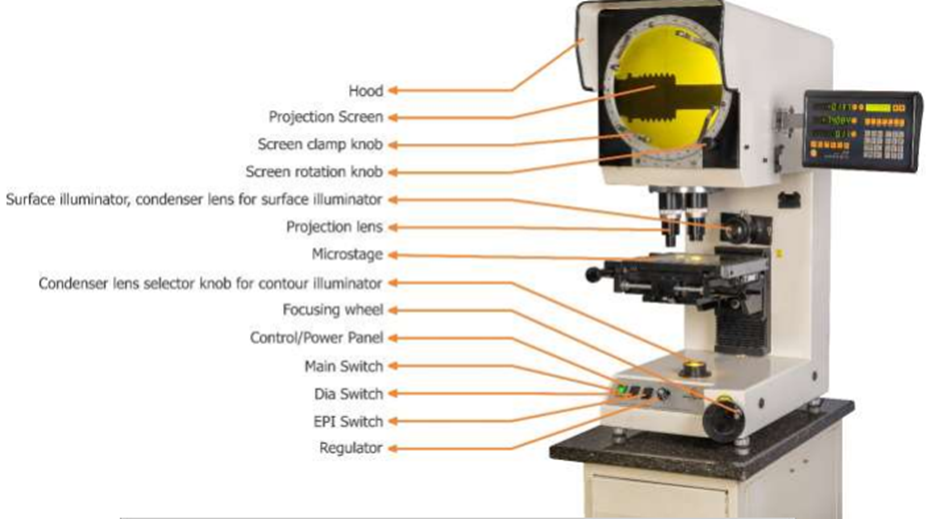
.jpg)
Profile Projector Diagram
A profile projector diagram illustrate the key components that enables its functionality. The main parts includes:
- Light Source- Typically a halogen, LED, xenon, or tungsten lamp that provide uniform illumination.
- Condenser Lens- Focus light into a parallel beam to enhance image clarity.
- Worktable/Stage- A glass or metal platform where the workpiece are placed, often equipped with micrometers or digital readouts for precise movement.
- Projection Lens- Magnify the workpiece’s shadow, typically offering 10x to 100x magnification.
- Mirrors- Reflects the light path to project the image onto the screen.
- Projection Screen: Display the magnified silhouette, often with a grid or crosshair for measurement.
- Fixtures/Clamps: Secures the workpiece to prevent movement during inspection.
- Digital Readout/Software: Modern systems includes digital displays or software for automated measurements.
The light pass through or around the workpiece, creating a shadow that is magnified by the projection lens and reflected by mirrors onto the screen, where measurements is taken.
Profile Projector Working Principle
The working principle of a profile projector is based on optics and shadow projection. Here’s how it works:-
- The part is placed on the stage (usually a glass plate).
- A light source beneath the part projects its shadow upward.
- This shadow passes through a system of lenses and is projected onto a ground-glass screen.
- The screen has a built-in grid or scale, which helps in comparing the dimensions of the object with tolerance limits.
By rotating or adjusting the lenses and mirrors, the user can observe different features of the component in a magnified form.
Types of Profile Projectors: Vertical vs. Horizontal
Profile projectors is classified based on their light path orientation: vertical profile projector and horizontal profile projector.
- Vertical Profile Projector:- The main axis are parallel to the projection screen, with light passing upward through a glass stage. This configuration is ideal for flat, lightweight parts like gaskets, electronics, or stamped components. Vertical projectors is compact and widely used for small workpieces.
- Horizontal Profile Projector:- The main axis is perpendicular to the screen, with light traveling horizontally. This setup suit heavier or larger parts, such as shafts, castings, or threaded components, which is clamped or held in a vise. Horizontal projectors often has larger screens (12–36 inches) and are preferred for complex or bulky workpieces.
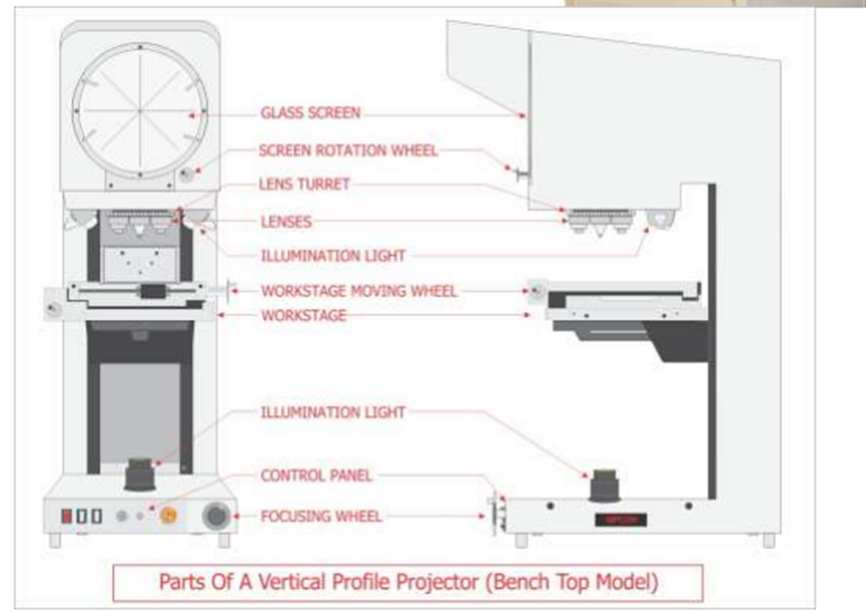
The choice between vertical and horizontal depend on the workpiece’s size, weight, and geometry. Vertical projectors excels for flat parts, while horizontal ones is better for cylindrical or heavy components.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Profile Projectors
Advantages
- Non-Contact Measurement:- Prevent damage to delicate or soft materials like rubber or thin electronics.
- High Precision:- Achieve measurements with a least count as low as 0.1–1 micron, ideal for tight tolerances.
- Ease of Use:- Require minimal training for traditional models, with intuitive silhouette-based inspection.
- Versatility: Suitable for complex shapes like gears, cams, threads, and molds, with magnification up to 100x.
- Digital Integration:- Modern digital profile projectors automates measurements, reducing operator error and increasing efficiency.
Disadvantages
- Limited to 2D Measurements:- Cannot measure depth or 3D features, restricting its use for complex geometries.
- Operator Skill Dependency:- Traditional models relies on operator expertise, which can affect accuracy.
- Image Distortion Risk:- Misalignment or lens imperfections may cause errors.
- Expensive Maintenance:- High-precision components require careful handling and periodic calibration.
- Limited Field of View:- Large parts may not fit on the worktable, necessitating multiple measurements.
Applications of Profile Projectors
Profile projectors are widely used across numerous industries. Here are some key applications of profile projector:
- Automotive: Measuring gaskets, piston rings, and gears
- Aerospace: Inspecting precision turbine components
- Plastic Injection Molding: Ensuring dimensional consistency
- Electronics: Checking PCB outlines and connector dimensions
- Medical Devices: Inspecting surgical components and prosthetics
- Tool and Die Making: Verifying die cuts and tool contours
Profile projectors are particularly valuable in industries where non-contact measurement are critical, such as for soft materials like rubber or delicate glassware.
Profile Projector Specifications
The profile projector specification vary by model but typically include:
| Feature | Specification |
| Magnification | 10x, 20x, 50x, 100x (interchangeable lenses) |
| Screen Size | 12–36 inches (up to 60 inches for large models) |
| Measuring Range | 50x50 mm to 400x300 mm |
| Least Count | 0.1–1 micron |
| Light Source | Halogen, LED, Xenon, or Tungsten |
| Stage Travel (X-Y) | 50–300 mm, with linear encoders |
| Digital Readout | Optional, with geometric measurement software |
| Weight Capacity | Up to 300 lbs for heavy-duty models |
| Optics | Telecentric for distortion-free projection |
| Illumination | Contour (bottom) and coaxial surface lighting |
Modern digital profile projectors incorporate high-resolution cameras, automatic edge detection, and software for instant measurements, enhancing accuracy and speed.
Digital Profile Projectors: The Modern Evolution
Digital profile projectors represents a significant advancement over traditional models. Equipped with high-resolution cameras, telecentric lenses, and software, they automates measurements, eliminate operator subjectivity, and supports 3D inspection to some extent. Systems like KEYENCE’s IM Series can measure up to 99 dimensions in seconds with ±0.7 µm accuracy. These projectors integrates with CAD files for direct comparison, streamlining quality control and reverse engineering. While more expensive, their speed, accuracy, and data analysis capabilities makes them ideal for high-volume production.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a vertical and horizontal profile projector?
A: A vertical profile projector has a light path parallel to the screen, ideal for flat, lightweight parts like gaskets. A horizontal profile projector has a perpendicular light path, suited for heavier or cylindrical parts like shafts, often with larger screens.
2. How does a digital profile projector improve over traditional models?
A: Digital profile projectors use cameras, software, and automatic edge detection to perform measurements faster and with higher accuracy (±0.7 µm). They reduce operator error, support CAD integration, and can handle complex parts more efficiently than manual models.
3. What are the main applications of a profile projector?
A: Applications of profile projectors include inspecting gears, threads, cams, and molds in industries like aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing. They are also used for reverse engineering and quality control.
4. How much does a profile projector cost?
A: The profile projector price depends on automation, depending on features like screen size, magnification, and software capabilities.
Q5: Can profile projectors be used for batch inspections in industries?
A: Yes, especially digital models are highly efficient for batch inspections as they allow fast and repeatable measurements with minimal operator intervention.
Final Thoughts on Optical Comparators
The Optical comparator or profile projector remain a vital tool in precision manufacturing., offering non contact, high accuracy measurement for a wide range of applications. Whether using a vertical profile projector for flat components or a horizontal profile projector for heavier part, these instruments ensures quality and compliance with strict tolerances. While traditional models is cost effective and simple, digital profile projectors enhances efficiency with automation and advanced software. By understanding the profile projector working principle, specifications, and advantages and disadvantages, manufacturers can selects the right tool to meet their needs, balancing profile projector price with performance.
Need help selecting the right Profile Projector?
Contact Presto at: +91 9210 903 903
Mail: info@prestogroup.com
Let us guide you with expert advice and the latest technology in measurement solutions!
Recent Blogs
- Moisture Meter: Types, Working Principle & Applications in Industrial Labs
- Environmental,Pharmaceutical, and Research Laboratories in BOD Incubator
- Vibration Tables Testing in Automotive and Aerospace Component
- Digital BS Testing Machines Features, Benefits, and Advantages
- Ways how TAPPI T811 ECT Tester Prevents Packaging Failure



