- /
- Blog / Autoclave: Definition, Principle, Parts, Uses, Applications
Autoclave: Definition, Principle, Parts, Uses, Applications

An autoclave is a machine used to sterilize equipment and materials with steam under high pressure. when water is heated inside the sealed chamber, the pressure rises and allows the temperature to get much hotter than normal boiling water. This high-temperature steam destroys bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even hardy spores.
Autoclaves are commonly used in hospitals, dental and medical clinics, laboratories, and research facilities—anywhere that absolutely clean, sterile tools are required. They’re valued for being reliable, powerful, and relatively low-cost compared to other sterilization methods.
Autoclave in Microbiology
The Auto-clave is thus indispensable for the maintenance of sterile conditions in microbiology, without which research and experiments cannot be conducted precisely. It is used to sterilize culture media, laboratory glassware, surgical instruments, pipette tips, and any other equipment coming into contact with microorganisms. Autoclaves in microbiology destroy all forms of microbial life, including the resistant bacterial spores; hence, they are the major implements in contamination prevention and in the generation of reliable experimental results.

Principle of Autoclave
Basically, the Autoclave principle applies steaming under pressure to get rid of the living organisms that could cause diseases.
How the Principle of Autoclave Works:
Water's boiling point is increased above 100°C by high pressure in the chamber. Indeed, the temperature can reach as high as 121°C at 15 psi or pounds per square inch.
This high pressure allows heat to completely permeate the substances quickly and deeply, hence enabling proper sterilization to be achieved.
By far, the most lethal agent to microbial proteins is water vapor, which causes them to coagulate and denature.
However, when the steam comes into contact with cooler surfaces, condensation occurs, releasing latent heat at a rate of 518 calories per gram which helps in the transfer of heat.
Typically, an autoclave runs for 15 to 30 minutes at a fixed temperature and pressure (depending upon the what is in it and how dirty it is, whether the vessel contains liquid or dry goods).
How Does an Autoclave Work?
Autoclaves run in three major cyclic phases:
- Purge Phase: Air in the sealed chamber is replaced by steam coming in through the sterilizer. For perfect sterilization, it is very important to remove air completely.
- Exposure Phase: The exhaust valve is closed and the temperature and pressure are increased to the predetermined value in the typical range of 121°C to 134°C. This temperature is held for a time rather long enough to carry out sterilization.
- Exhaust Phase: During this stage, the exhaust valve opens and steam is vented out as the pressure and temperature inside the chamber slowly fall back to ambient levels. Then they are dried and cooled before being taken out.
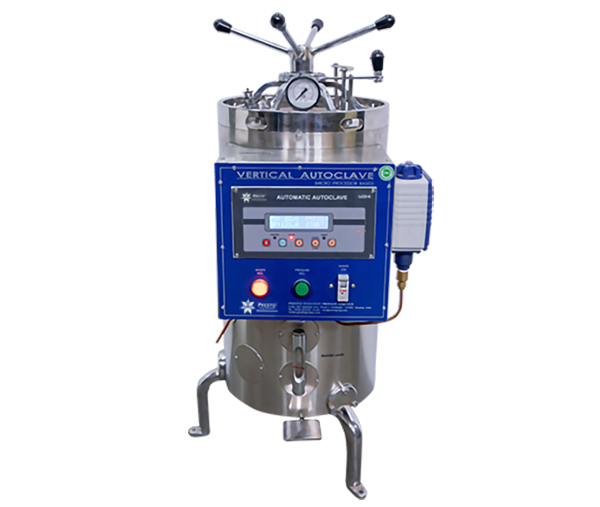
Autoclave Parts and Components
The understanding of the autoclave diagram and its component members assists in good operation and maintenance.
Key parts include:
- Pressure Chamber: It is composed of an inner chamber which is typically stainless steel or gunmetal and an outer jacket which is made of iron. The materials to be sterilized are placed in the inner chamber, while steam resides in the outer jacket that facilitates heat transfer and reduces sterilization time. Chamber are available in sizes from 100L to 3000L.
- Lid/Door: Closes the chamber to the external atmosphere for providing the required conditions of temperature and pressure. It comprises:
a)Pressure Gauge: Indicates the rise in pressure within the chamber.
b) Whistle: Controls pressure by blowing off excess steam.
v) Safety Valve: It has a layer of rubber which, in case of malfunction, bursts to let the pressure out and avoid explosions. - Steam Generator/Electrical Heater: This is located at the bottom of the chamber and is used to heat up the water to create steam. The water level must not be too low in order to avoid burning or malfunction.
- Vacuum Generator: Some models of the autoclave feature this, which removes air pockets from the chamber so that complete sterilization may be realized.
- Wastewater Cooler: Cools effluent (air, steam, and condensate) before discharge through drainage piping to eliminate damage from very hot water.
- Thermostat and Timer: The thermostat triggers the timer when the desired temperature is reached, typically set for 15-20 minutes depending on the load.
Types of Autoclaves
Presto Autoclave and Sterilizers come in several varieties, depending on the sterilization methods employed:
- Gravity Autoclaves (Class N): They are the simplest and least expensive type of autoclaves steam is introduced either from the top or sides, pushing the air down and out through vents at the bottom. Good for sterilization of all non-porous materials e.g. stainless steel instruments, glassware, biohazard waste, and packaged materials.
- Pre-Vacuum Autoclaves (Vacuum-Induced): A vacuum system completely removes the air before the steam enters; hence, deeper steam penetration is achieved. Applications include porous items, wrapped surgical kits, animal cages, bedding, and other items with hard-to-reach internal spaces.
- Vertical Autoclaves: Compact units with top-loading design, common in small laboratories and clinics.
- Horizontal Autoclaves: These are front-loading units for large sterilization loads within hospitals and pharmaceutical industries.
Use and Applications of an Autoclave
The usage of autoclaves ranges in various sectors:
Medical and Healthcare Applications:
- Sterilizing surgical instruments, scalpels, forceps, and scissors
- Decontamination of medical waste prior to disposal
- Sterilization of implants, catheters, and surgical drapes
- Processing laboratory equipment and glassware
- Sterilization of dental instruments in dental clinics
Laboratory Applications:
- Sterilization of culture media and agar plates
- Decontaminating biohazardous waste
- Sterilization of pipette tips, tubes, and flasks
- Processing animal cages and bedding in research facilities
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology:
- Sterilization of containers and process equipment
- Processing components for vaccine development and biologic drug production
Food Industry:
- Sterilization of utensils used in food processing and packaging
Why the Presto Group Autoclave is Essential for Medical, Scientific, and Industrial Use
The Presto Group autoclave is a significant equipment that is now a must-have in the current medical, scientific, and industrial fields. Based on the principle of autoclave moist heat sterilization under pressure, it achieves the destruction of all harmful microorganisms. You need to be familiar with the autoclave parts via an autoclave diagram, understand the proper use of the autoclave, and know which type of autoclave is suitable for your needs. There is a good selection of autoclaves to choose from, both basic and more sophisticated models, providing this essential technology for any size facility to help keep things sterile and avoid infections.
Looking for a trustworthy autoclave manufacturer with competitive price?
Contact our experts today to identify the best autoclave for your applications. Ring us at +91 9210 903 903 or send an e-mail at info@prestogroup.com to ask for a quotation and further information!
Recent Blogs
- Controlled Humidity Chamber: Environmental Testing Methods, Applications & Packaging Testing Use Cases
- Spectrophotometer & Portable Spectrophotometer: Working Principle and Laboratory Applications
- Paint Tester & Coating Testing Equipment: Types, Testing Process, and Industrial Applications
- Moisture Meter: Types, Working Principle & Applications in Industrial Labs
- Environmental,Pharmaceutical, and Research Laboratories in BOD Incubator



