

In material science and protective coatings, corrosion resistance is not a luxury but an indispensable one. From automotive components battling road salt to electronics facing marine environments, products have to be robust enough to deal with very aggressive chloride conditions to serve long. In this very vein, the necessity of a salt spray test and a standardized process for evaluating durability of any product will become evident.
When working in the quality assurance or research and development department, it's so important to understand the exacting procedures laid out in the documentation of these standards.
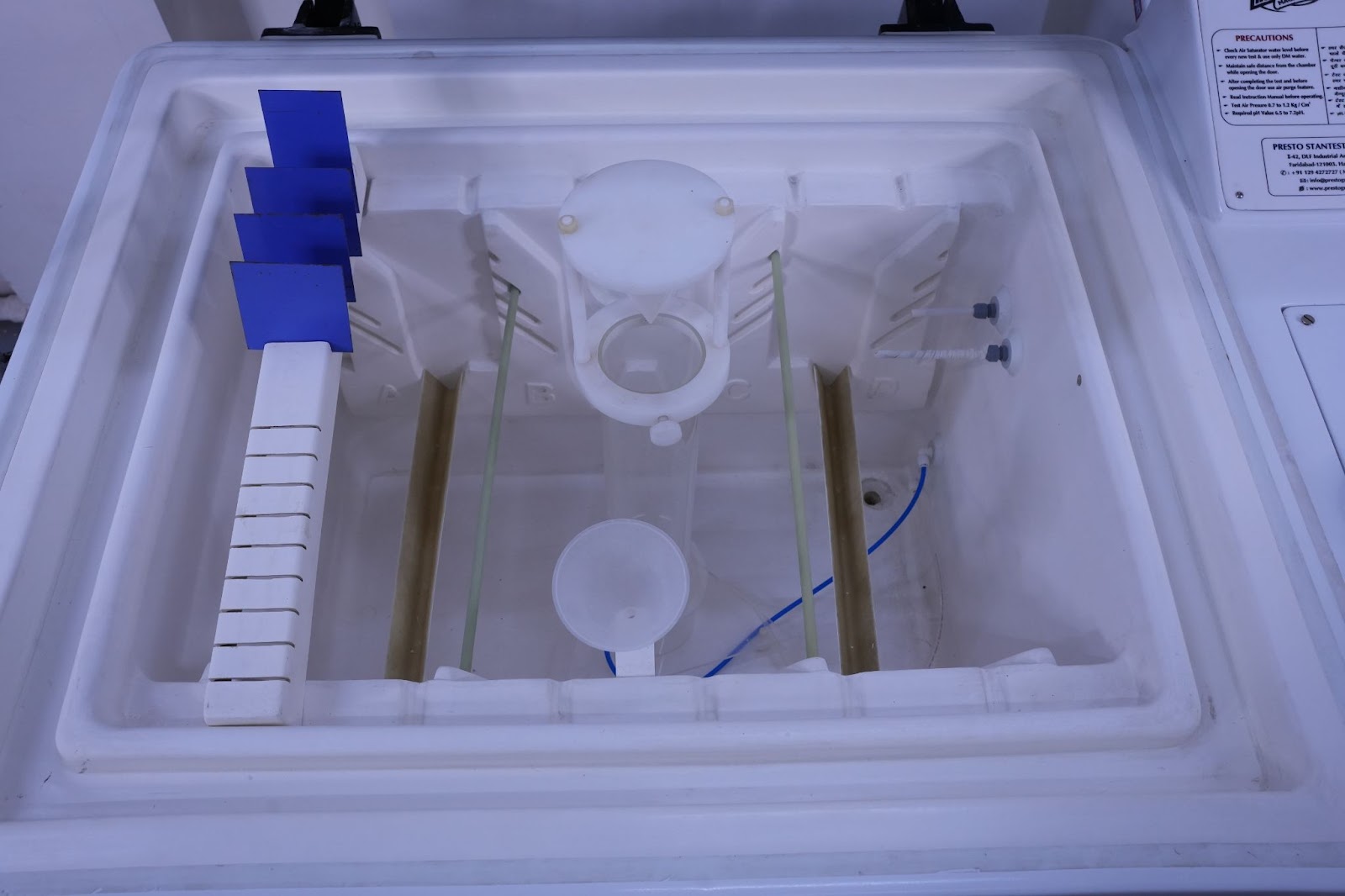
What: The Salt Spray or Salt Fog test is one of the most standardized forms of Accelerated Corrosion testing; it consists of the exposure of coated or uncoated metallic specimens to a concentrated continuous mist of salt water within a controlled environment, usually at a specialized salt spray chamber. This controlled exposure simulates years of potential damage from a saltwater-laden atmosphere condensed into mere hours or days of testing.

Who: Manufacturers of materials and coating applicators in various industries like automotive, aerospace, marine, construction, and electronics use this test. Any company that relies on product integrity to withstand a chloride environment should be using the salt test procedure in their QC program. Many times, companies will ship their samples to an accredited salt spray testing lab for rigorous adherence to protocol, along with independent third-party verification.
Results from a salt test standard offer the possibility of making relative comparisons between different materials, coatings, or process variants. Although the test does not predict the precise service life in a specific natural environment, it serves as one of the most valuable means for quality control, material screening, and assurance of reproducibility in manufacturing processes.
ASTM B117 Standard: The American Benchmark
Test Specification: An Agilent value is assigned to the Salt Spray Apparatus Standard Practice ASTM B117, which is used all over the world and used generally in a multitude of industry-specific tests.
ISO 9227: The International Counterpart
The primary international standard for the procedure covered under this test is the ISO 9227 standard: Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres - Salt spray tests. This test includes the The Neutral Salt Solution (NSS) test along with Acetic Acid Salt Spray (AASS) and Copper Acetic Acid Salt Spray (CASS) tests, has been accepted for various decorative and protective coatings containing copper, nickel or chromium.
NSS Test Conditions: The same as ASTM B117; 5% NaCl, pH 6.5 - 7.2 and 35°C (± 2°C).
Angle of Specimen: The test specimens must be mounted at angle from 15 to 25 degrees from vertical.
AASS / CASS: The AASS / CASS variation is run at higher temperatures (e.g., 50°C for CASS) with an acidified salt solution causing the process to speed up for some types of coatings.
The following procedures should be regarded as generic operations to which no variation should occur in the salt spray testing laboratory. If required, wax or tape edge protection should be applied according to the conditions outlined in the test procedure.
1. Salt Solution Preparation
Prepare a salt solution with 5% concentration by mass of high-purity sodium chloride in purified water. More important is the requirement that its pH be adjusted within the range of 6.5 and 7.2 for NSS with the use of reagent-grade hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide.
2. Preparing the Salt Soln.
The specimen must be appropriately located within the salt spray chamber. All specimens should be located at the angles described (15º to 30º for B117 and 15º to 25° for 9227) and configured so that they do not actually touch each other or the walls of the chamber. Condensate from one specimen should also not drip on another, since this could falsify the outcome of the test. The chamber temperature and the air saturator must be set and stabilized.
3. Continuous Spraying and Monitoring
Atomization of the salt solution starts, and the corrosive fog is generated. Operators are supposed to check and confirm some key test parameters periodically during the tests, which include chamber temperature and air pressure, among others; besides the salt fog collection rate during the test. This guarantees the test environment retains its accuracy throughout the entire testing period, which may range from 24 hours to 1000 hours or greater as dictated by the product specification.
5. Assessment and Reporting
Once the time frame of exposure is completed, the samples will be removed, rinsed to eliminate excess salt and dried. The corrosion resistance of the material is then evaluated. This normally consists of a visual examination for corrosion- either in the form of red rust on steel or white rust on zinc, blistering, or deterioration of the coating. The final test report needs to state all the conditions that prevailed during testing and the results obtained, which serves as an important comparative measure in quality control and R&D work. Accordingly, data integrity is ensured by following the standard for the salt test.
Get high-quality, ASTM B117 & ISO 9227 compliant Salt Spray Chambers from Presto Group – India’s trusted testing instrument manufacturer.
Call now: +91 9210 903 903
Email: info@prestogroup.com
Know more about our Salt Spray Chamber Price, models, and features today!