- /
- Blog / Tensile Strength and Yield Strength: Definitions, Differences, and Applications
Tensile Strength and Yield Strength: Definitions, Differences, and Applications

When engineers design bridges, skyscrapers, or aircraft, they rely on a deep understanding of material properties to ensure safety and performance. Two key metrics, tensile strength and yield strength, define how materials handle forces that try to stretch or deform them. These properties aren’t just numbers—they dictate whether a steel cable will snap or a beam will bend permanently. This blog dives into what these terms mean, how they differ, and where they matter most, covering tools like the tensile strength tester, the tensile strength formula, the tensile strength unit, and the tensile strength test. We’ll also explore tensile strength vs yield strength and zoom in on tensile strength steel, a material that shapes our world.
What Does Tensile Strength Mean?
Picture a rope in a tug-of-war: how much force can it take before it snaps? That’s the essence of tensile strength—the maximum stress a material can endure while being pulled before it breaks. It’s a measure of toughness under tension, critical for elevator cables or parachute cords.
The tensile strength formula is straightforward:
Tensile Strength = Maximum Load / Original Cross-Sectional Area
Tensile Strength = Maximum Load (N) ÷ Original Cross-Sectional Area (mm²)
This gives the force per unit area at the breaking point, measured in tensile strength units like Megapascals (MPa) or pounds per square inch (psi). For tensile strength steel, values vary: mild steel hits ~400 MPa, while high-strength alloys can exceed 2000 MPa, thanks to alloying and processing.
Yield Strength: The Point of No Return
Now imagine that rope stretching but not snapping. Up to a point, it bounces back to its original length. Beyond that, it’s permanently stretched. That threshold is yield strength—the stress where a material starts to deform plastically, losing its original shape.
Yield strength is about resilience, not failure. For ductile materials like steel, it’s lower than tensile strength, allowing some give before breaking. Brittle materials, like glass, have less room, with yield and tensile strengths often closer.
Tensile Strength vs Yield Strength: What’s the Difference?
The debate of tensile strength vs yield strength hinges on purpose:
- Tensile Strength: Peak stress before fracture, about surviving extreme pulls.
- Yield Strength: Stress where permanent deformation starts, about staying functional.
- Applications: Cables that can’t break need high tensile strength; columns that can’t bend need high yield strength.
- Testing: A tensile strength test measures both—tensile strength at fracture, yield strength at plastic strain onset (often 0.2% for metals).
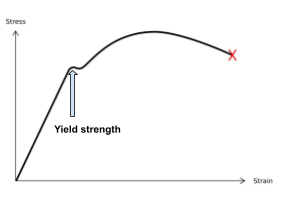
In tensile strength steel, a high-strength grade might have 1500 MPa tensile strength and 1200 MPa yield strength, showing ductility. Brittle materials often break with little warning.
How a Tensile Strength Test Works
A tensile strength test stretches a sample until it breaks, using a tensile strength tester. This machine pulls the specimen apart while tracking force and stretch, producing a stress-strain curve.
Tensile Strength Tester Working Principle
The tensile strength tester working principle centers on precision. The machine includes:
- Grips to hold the specimen.
- A load cell to measure force.
- An extensometer to track stretch.
- A control system to apply force and log data.

As it pulls, the machine plots a curve showing:
- Elastic zone: Where the material snaps back.
- Yield point: Where permanent deformation begins (yield strength).
- Peak stress: Ultimate tensile strength.
- Breaking point: Tensile strength.
Modern tensile strength testers use software for detailed analysis, vital for materials like tensile strength steel.
Where These Properties Shine
Tensile Strength in Action
Tensile strength is key when materials face pulling forces:
- Construction: Steel cables in bridges like the Golden Gate use tensile strength steel to resist snapping under weight and wind.
- Aerospace: Aircraft wings need high tensile strength to handle flight stresses.
- Manufacturing: Plastic films and fabrics rely on tensile strength for durability.
Yield Strength’s Role
Yield strength prevents unwanted deformation:
- Buildings: Columns need high yield strength to stay rigid.
- Cars: Frames use steel with strong yield strength to resist crumpling in crashes.
- Pipelines: Pipes must resist yielding under pressure to avoid leaks.
For tensile strength steel, alloys and heat treatments balance these properties. Cold-drawn steel boosts tensile strength for wires; tempered steel enhances yield strength for structures.
What Affects These Strengths?
Factors shaping tensile and yield strengths include:
- Alloys: Carbon or chromium boosts steel strength.
- Processing: Quenching refines microstructure for strength.
- Temperature: Heat weakens steel, critical in fires.
- Loading Speed: Fast pulls can increase apparent strength.
- Flaws: Cracks or inclusions reduce tensile strength.
Tensile Strength Steel in Focus
Tensile strength steel is engineering’s backbone. The tensile strength test, guided by standards like ASTM E8, uses precise samples for accurate results. These tests help select steel for skyscraper cables or jet components. High-tensile steel in bridges withstands wind and weight, while ultra-tough steel in planes cuts weight without sacrificing safety.
Why Choose Presto Stantest Pvt. Ltd. Tensile Strength Tester?
Presto Stantest Pvt. Ltd., a leader in testing instruments, offers advanced tensile strength testers trusted by giants like Havells and Amazon. Their digital models, like the TTM series, use the Constant Rate of Traverse (CRT) principle for precise testing of materials like steel, plastics, and textiles. Features include advanced load sensors, no-slippage grips, and bright LED displays for accurate results. With over 40 years of expertise, Presto’s testers meet standards like ASTM D412, ensuring reliability. Their robust design, safety features like over-travel protection, and global support make them ideal for quality control in industries worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions About Tensile Strength Tester (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between tensile strength and yield strength?
Ans: Tensile strength is the maximum stress a material can take before breaking, while yield strength is where it starts to deform permanently. One’s about breaking, the other’s about bending.
Q2: How does a tensile strength tester work?
Ans: A tensile strength tester pulls a sample apart, measuring force and stretch. Its working principle uses grips, a load cell, and an extensometer to create a stress-strain curve.
Q3: What’s the tensile strength formula and its unit?
Ans: The tensile strength formula is Maximum Load divided by Original Cross-Sectional Area. The tensile strength unit is usually Megapascals (MPa) or psi.
Q4: Why does tensile strength matter for steel in construction?
Ans: Tensile strength steel ensures components like cables and beams handle pulling forces without breaking, keeping structures like bridges and towers safe under heavy loads.
Wrapping Up
Tensile strength and yield strength define how materials endure stress, shaping safe and efficient designs. The tensile strength formula and tensile strength unit provide clear metrics, while the tensile strength tester and its working principle deliver data. Knowing tensile strength vs yield strength guides the use of tensile strength steel in bridges, planes, and more. These properties make our built world possible.
Looking for the Best Tensile Strength Tester Price?
Get accurate and reliable testing solutions at the most competitive tensile strength tester price. Contact us today to request a quote or get more information.
Call Now: +91 9210 903 903
Email: info@prestogroup.com
Don't miss out on precision testing instruments trusted by top manufacturers!
Recent Blogs
- Compression Testing Machine Operating Method & Packaging Strength Testing Applications
- Bottle Cap Torque Tester Digital Torque Testing for Packaging Quality Control
- Controlled Humidity Chamber: Environmental Testing Methods, Applications & Packaging Testing Use Cases
- Spectrophotometer & Portable Spectrophotometer: Working Principle and Laboratory Applications
- Paint Tester & Coating Testing Equipment: Types, Testing Process, and Industrial Applications



