

A spectrophotometer is a tool that tells how much light is absorbed by any liquid or substance. It do this by passing different colour lights through the sample. It is mostly used in chemistry, biology, environmental science, and other subjects also.
We use it to know things like how much DNA is in the sample, how much chemical is present or to check if the product colour is proper or not. That’s why it is used in science lab and also in industries.
In this article, we will learn how spectrophotometer works, what are it's types and where it is used in real life. Also we will see the proper way to use it and some tips also to get good result.
The principle of a spectrophotometer is based on the absorption or transmission of light by a substance at specific wavelengths. When a beam of light passes through a sample, certain wavelengths are absorbed while others are transmitted. This interaction depends on the molecular structure and concentration of the substance.
.png)
A spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light before and after it passes through the sample. It uses a light source, a monochromator to isolate specific wavelengths, a sample holder, and a detector. The monochromator ensures that only the desired wavelength reaches the sample, and the detector records the amount of light absorbed or transmitted.
The key formula used is Beer-Lambert Law, which states:
A = εlc
Where:
A = Absorbance
ε = Molar absorptivity
l = Path length
c = Concentration of the solution
This law helps quantify the concentration of the analyte based on the measured absorbance.
Let’s understand the working of a spectrophotometer using a simplified spectrophotometer diagram:
[Light Source] → [Monochromator] → [Sample Cuvette] → [Detector] → [Readout Display]
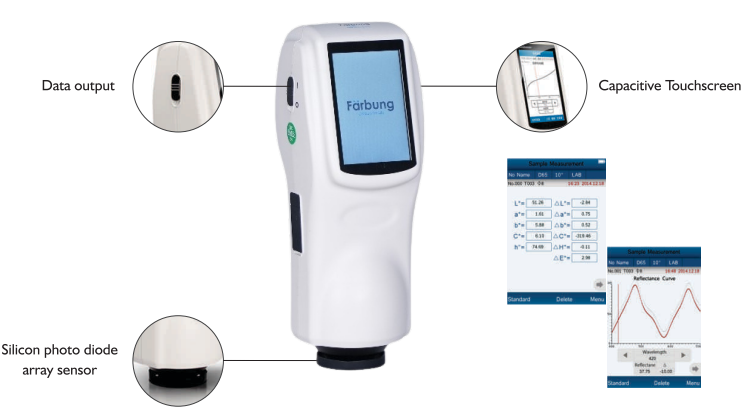
Main Components:
Working Steps:
This reading helps determine the concentration or characteristics of the solution being tested.
There are several spectrophotometer types depending on light range and beam configuration:
Measures absorbance in the UV (190-400 nm) and Visible (400-700 nm) spectrum.
Widely used in analytical labs.
Works in the infrared region (700 nm – 1 mm).
Used for analyzing molecular vibrations and structures.
Uses a single light path; compares sample and blank manually.
More affordable but less accurate.
Splits light into two beams (sample and reference).
Provides better accuracy and stability.
Here is the general spectrophotometer procedure followed in laboratories:
1. Warm-Up
Turn on the device and let it stabilize (usually for 15-20 minutes).
2. Select Wavelength
Choose the appropriate wavelength specific to your test substance.
3. Blank Calibration
4. Sample Measurement
5. Record and Repeat
Learning how to use a spectrophotometer effectively ensures accurate and repeatable results. Follow these tips:
The spectrophotometer uses are vast and span across many scientific and industrial fields:
While powerful, spectrophotometers also come with a few limitations:
Digitalization and miniaturization modern spectrophotometers are becoming more compact, portable, and automated. Some models now integrate with cloud based platforms, allowing real time data sharing and remote monitoring.
Additionally integration with AI and machine learning will enable predictive analysis, improved accuracy, and quality control in manufacturing and laboratory environments.
Need help? Our team is just a call away.
Spectrophotometers are very important tools in today's testing world because they help in accurate analysis of chemical, biological, and also materials properties. It's capability to measure light absorption with very high precision makes it unreplaceable in research works, production processes and also for quality checking. Whether it is checking the concentration level or making sure the product is looking same always, spectrophotometers do the job perfectly. It give trustworthy and repeatable results which are backed by science in many types of industries.
Q1: What are the main types of spectrophotometers available?
Ans: There are several types of spectrophotometers, including UV-Visible, IR, Single Beam, and Double Beam spectrophotometers. Each type is designed for specific applications.
Q2: How do you use a spectrophotometer step by step?
Ans: To use a spectrophotometer:-
Q3: What is the procedure for using a spectrophotometer in a lab?
Ans: Turn on the spectrophotometer, select the wavelength, calibrate with a blank, then insert the sample. The device measures light absorption to help find the sample’s concentration or content.
Q4: What are the most common applications of spectrophotometers?
Ans: Spectrophotometers are widely used in life sciences, chemistry, environmental testing , food industry, and pharmaceuticals.
Q6: How do you maintain and clean spectrophotometer?
Ans: For cleaning, always use soft lint-free tissue to wipe cuvette holder. Make sure cuvettes are clean and don’t have any scratches. Avoid touching optical parts with bare hands. Follow manufactures instructions for routine cleaning and calibration.
Need help? Our team is just a call away.
Presto Group is a well-known company that makes and supplies high-quality spectrophotometers. Our machines are used by top labs and industries for accurate and reliable results.
Need help choosing the right spectrophotometer or want to know the price? Our team is ready to help you find the best one for your needs.
Call us at +91 9210 903 903 | Email: info@prestogroup.com