- /
- Article / What is a Fume Hood? Diagram, Working Principle, Types, and Uses
What is a Fume Hood? Diagram, Working Principle, Types, and Uses

Ever walked into a chemistry lab and seen that big glass fronted box with a humming sound? Kinda looks like something from a science fiction movie, right? That thing is a fume hood your best friend when it comes to staying safe while handling stinky or dangerous chemicals. Whether you're a student messing around with test tubes or a pro researcher mixing hardcore stuff, knowing how a fume hood works is kinda a must.
In this blog, I’ll try to explain everything you should know about a fume hood—how it works, what parts it has, the types out there, and why labs can’t live without one. I'll also add a small table and answer a few FAQs at the end so it's easier to get it all.
What Exactly is a Fume Hood?
Picture this: you’re mixing some chemicals that give off funky, potentially toxic fumes. Without proper protection, you’d be coughing up a storm—or worse. That is where a fume hood comes in. It is basically a ventilated box that sucks up and safely removes harmful fumes, gases, vapors, dust from your workspace. Think of it as a shield between you and the nasty stuff you’re working with. Also called a chemical hood or fume cupboard, it’s a must-have in labs dealing with volatile or toxic substances, like those in chemistry, pharmaceuticals, or even forensics.

A typical fume hood is a large, enclosed workstation with a transparent, movable sash (think of it as a window) that lets you reach in while keeping dangerous stuff contained. It’s usually set at a comfy standing height—about 28 to 34 inches off the floor—and comes in sizes wide enough for one to three people to work at (from 1000 mm to 2000 mm). The whole setup is designed to keep you safe while you tinker with chemicals that could otherwise ruin your day.
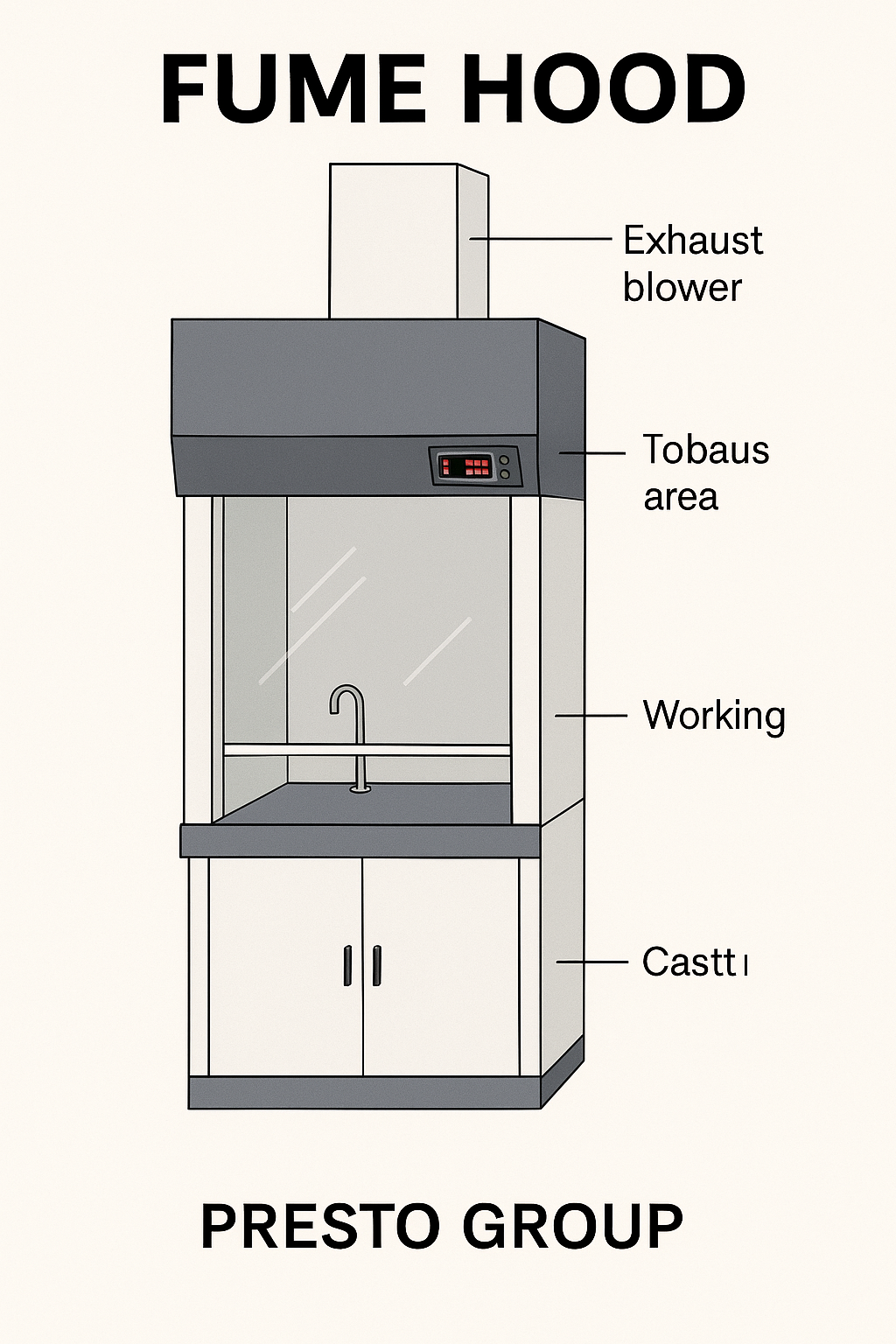
Fume Hood Diagram
A fume hood diagram shows the main parts of a fume hood, like the glass window (sash), fan, vents, and work area. It helps explain how the fume hood pulls out harmful gases and keeps the air clean. This simple diagram helps students and lab workers understand how the fume hood works and how to use it safely.
How Does a Fume Hood Work?
It’s all about airflow. When the sash is open, the hood pulls in room air—like a mini vacuum cleaner—and creates a low-pressure zone inside. That keeps any dangerous vapors or particles from floating into your face.
Depending on the type:
- Ducted fume hoods send the dirty air outside the building.
- Ductless fume hoods clean the air using filters (like HEPA or carbon) and send it back into the room.
Most hoods aim for a face velocity (air speed) of 80–120 feet per minute. And yeah, good ones come with alerts if the airflow drops. Safety first!
Breaking Down the Parts of a Fume Hood
Each part of a fume hood has a specific job to keep you safe. Here’s a quick rundown in a table for clarity:-
| Part | What It Does |
| Sash | Protects you from fumes and splashes while letting you reach inside. |
| Work Surface | Gives you a sturdy, chemical-proof spot to do your experiments. |
| Baffle System | Guides airflow to evenly pull out fumes and keep things safe. |
| Exhaust Fan | Sucks air through the hood and sends it out or through filters. |
| Airfoil | Smooths out airflow at the entrance to avoid turbulence. |
| Control Panel | Lets you tweak fan speed, lights, and check if everything’s running smoothly. |
| Ducting/Filters | Either vents air outside (ducted) or cleans it for recirculation (ductless). |
These parts team up to make sure your lab stays a safe place to work, no matter how sketchy the chemicals you’re handling.
Types of Fume Hoods
Not all fume hoods are created equal. There are several types, each built for specific jobs:
- Ducted Fume Hoods: These are the heavy hitters, venting fumes straight out of the building through ducts. They’re perfect for labs dealing with all sorts of toxic or smelly chemicals.
- Ductless Fume Hoods: These use filters to clean the air and pump it back into the lab. They’re easier to install and save energy, but they only work for specific chemicals that their filters can handle. Fun fact: about 22% of fume hoods are ductless, per a 2010 survey.
- Downflow Fume Hoods: Built for powdery stuff, these pull air downward through slits in the work surface. They Are similar to laminar flow cabinets but focus on keeping you and the environment safe.
- Perchloric acid Fume Hoods: These are super specialized, with wash-down systems to prevent dangerous buildup when working with perchloric acid (which can be explosive if not handled right).
- Variable Air volume hoods: Smarter and more energy-efficient, these adjust airflow based on how open the sash is, keeping face velocity steady while saving power.
- Canopy Hoods: Less common in labs, these are used for capturing heat or non-toxic fumes, often in industrial settings.
Choosing the right one depends on what you’re working with and your lab’s setup.
Why Do Labs Need Fume Hoods?
Fume hoods are like the superheroes of lab safety. Here’s what they’re used for;
- Handling Sketchy Chemicals- If you’re working with stuff like nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid, or anything that smells like trouble, a fume hood keeps those vapors from getting to you.
- Pharma Work- In drug research, fume hoods protect you while you mix sensitive compounds or handle potentially dangerous ingredients.
- Some Bio Work- With the right filters, they can handle certain biological agents, though they’re not as good as biosafety cabinets for pathogens.
- Keeping the Environment Safe- By venting or filtering harmful stuff, they stop toxins from polluting the lab or beyond.
- Teaching Labs- In schools, they let students experiment with chemicals safely, keeping everyone compliant with safety rules.
If a chemical’s Safety Data Sheet (SDS) says “toxic by inhalation” or “avoid breathing fumes,” you’ll want a fume hood nearby.
Fume Hood vs. Biosafety Cabinet vs. Laminar Flow Hood
Fume hoods get mixed up with other lab gear all the time, so let’s clear the air:-
Fume Hood vs. Biosafety Cabinet:- Fume hoods are all about protecting you from chemical fumes by pulling air in and venting it out. Biosafety cabinets (BSCs) protect you, your samples, and the environment from biological nasties like bacteria or viruses, using HEPA filters. BSCs come in different classes (I, II, III), with some protecting your samples too. Fume hoods? Not sterile, so don’t expect them to keep your samples germ-free.
Fume Hood vs. Laminar Flow Hood:- Laminar flow hoods blow clean, filtered air outward to keep your samples (like cell cultures) free from contamination, but they don’t protect you from hazardous stuff. Fume hoods pull air inward to keep you safe from chemicals but won’t keep your workspace sterile.
FAQs About Fume Hoods
Q1: What is the main job of a fume hood?
A: It’s there to keep you safe from harmful fumes, gases, or dust by trapping and removing them. It also acts as a barrier against spills or small explosions.
Q2: How often should you check a fume hood?
A: Get it inspected once a year to make sure the airflow’s on point (80–120 FPM). Most hoods have a sticker showing the last inspection date.
Q3: Can I use a fume hood for biological experiments?
A: Not really. Fume hoods aren’t sterile and don’t protect against pathogens. For bio work, you’re better off with a biosafety cabinet.
Q4: What is the deal with ducted vs. ductless fume hoods?
A: Ducted ones vent fumes outside through pipes, making them versatile for all kinds of chemicals. Ductless ones filter air and release it back into the lab, but they only work for specific chemicals their filters can handle.
Clean Air, Safe Labs: The Fume Hood Recap
A fume hood is a vital lab tool designed to keep harmful fumes away from users by drawing in contaminated air and venting it outside. It has key parts like a sash (glass window), exhaust fan, and airflow system. By using a fume hood, scientists can safely handle chemicals without breathing in toxic vapors—keeping both the lab and its workers safe and healthy.
Fume Hood Price in India – What to Expect?
Fume hood Prices vary depending on type, size, and features. Ductless ones may be cheaper upfront but cost more over time (because of filters). Ducted ones are a bit more complex to install.
If you wanna know the exact cost, just give us a call.
Where to Buy?
You can reach out to Presto Stantest, one of India’s trusted lab equipment suppliers. They’ve got reliable, customizable fume hoods for all kinds of labs.
Email: info@prestogroup.com
Call: +91 9210 903 903


