
.png)
pH measurements are essential for quality and accuracy control in the laboratories of chemistry, biology, agriculture, water treatment and food processing. The pH meter is an important analytical device used in determination of acidity or alkalinity in solutions. Test your drinking water, soil, or industrial fluid and a pH meter will provide you with accurate results and uniform supervision.
In this blog, we’ll explores the pH meter principle, its types, working mechanism, digital pH meter diagram, and common applications. We’ll also provide a simple step-by-step procedure of pH meter usage, a comparison table, and frequently asked questions.
A pH meter is a scientific instrument that accurately measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, helping industries, laboratories, and agriculture maintain quality, safety, and precise chemical balance. It determine the hydrogen ion concentration (pH) and provides accurate readings, usually on a scale of 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, values below 7 are acidic, and above 7 are alkaline. The instrument typically consists of a probe (electrode) and a digital display. It is widely used in laboratories, agriculture, water treatment, food production, and chemical industries. Accurate pH measurement is essential for quality control, chemical reactions, and environmental monitoring, making the pH meter a valuable analytical tool.
It expresses how acidic or basic the solution is, on a scale of 0 to 14:
The device displays this measurement digitally or via analog output, depending on the model.
.png)
A pH meter is a laboratory equipment to measure the pH (acidity or alkalinity) value of a liquid. It is because the measurement is indicated on the pH scale which ranges from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very basic), where 7 is the neutral point.
The full form of pH meter is “Potential of Hydrogen Meter.” It is used to measure the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, indicating its acidity or alkalinity for laboratory, industrial, and agricultural applications.
The PH meter working principle is based on electrochemical potential difference. It compares the voltage between two electrodes—-the glass electrode (measuring electrode) and the reference electrode. When immersed in a solution, the glass electrode develops a potential relative to the pH of the solution. The reference electrode maintains a constant potential.
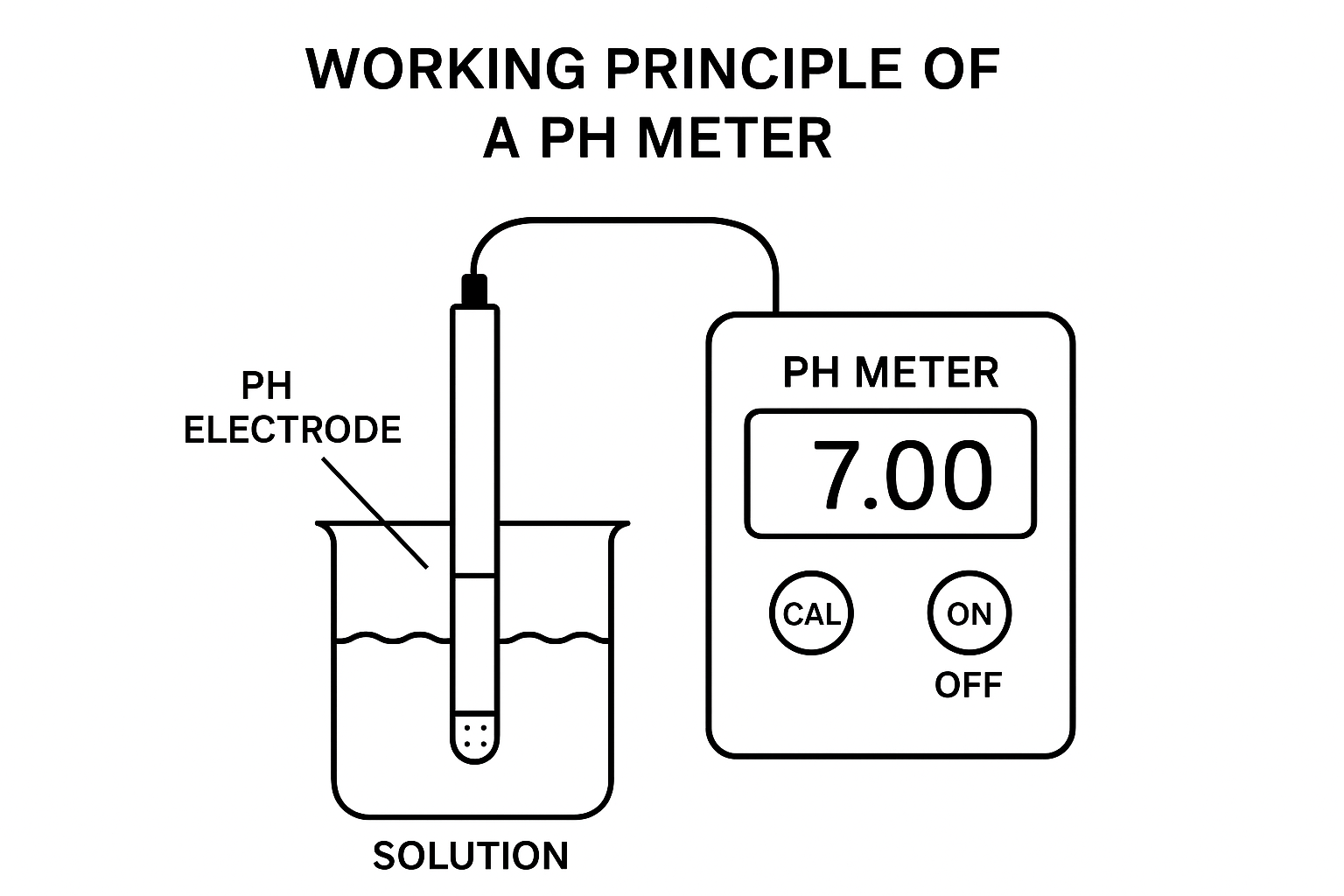
The pH meter amplifies the difference and converts it into readable pH units.
Formula Used:
E = E₀ + (2.303 × RT/nF) × log [H⁺]
Where:
Analogy
Consider a pH-meter as an ultrasensitive voltmeter for the chemistry world. Rather than measuring the voltage of a battery, it measures the minuscule "chemical-voltage" that is generated by the acidity in a solution.
A typical pH meter consists of the following parts:
| Component | Description |
| Glass Electrode | Senses the hydrogen ion activity in the solution. |
| Reference Electrode | Maintains a stable potential for comparison. |
| Temperature Sensor | Compensates for temperature variation during measurement. |
| Display Unit | Digital or analog readout showing the pH value. |
| Amplifier Circuit | Amplifies the millivolt signal from electrodes. |
| Calibration Knobs | Used for setting standard readings before actual measurement. |
Different types of pH meters are used for specific applications:
1. Digital pH Meter
2. Portable/Handheld pH Meter
3. Pen-type pH Meter
4. Benchtop pH Meter
5. pH Transmitters
| Type | Accuracy | Portability | Application |
| Digital | High | Medium | Labs, Food, Beverages |
| Handheld | Medium | High | Agriculture, Field Testing |
| Pen-type | Low to Medium | Very High | Pools, Aquariums, Home |
| Benchtop | Very High | Low | Pharmaceuticals, Research Labs |
| Industrial/Online | Very High | Fixed Installation | Water Plants, Process Industries |
Below is a simplified diagram of a digital pH meter's internal structure:
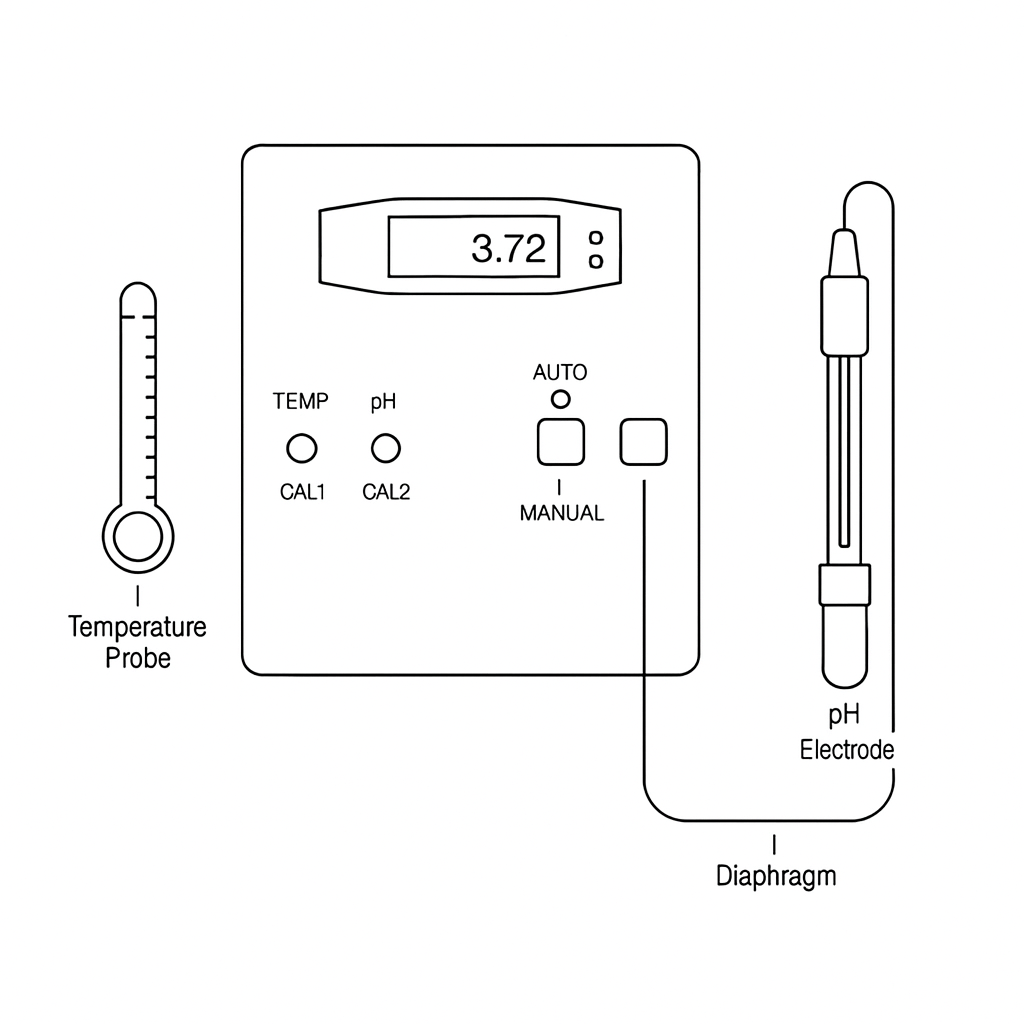
This diagram helps understand how a digital pH meter integrates its core components to give accurate measurements.
When the electrodes are immersed in a solution:
Modern pH meters often come with auto-calibration, temperature compensation, and data logging features.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to operating a pH meter correctly:-
Calibration
Measurement
Cleaning and Storage
The pH meters have found their wide applications in labs also for the precise determination of acidity and alkalinity of various solutions. In research, they can be used to study chemical reactions, monitor buffer solutions, and maintain exact pH levels for experiments. In pharmaceutical laboratories, pH meters are essential in pharmaceutical formulation, stability testing and quality assurance. They are used in biological and microbiological laboratories for testing culture media, enzymes and cell growth conditions, areas where the pH directly affects the outcome. They are also used in the food and beverage industry laboratories to check for freshness of the products, fermentation procedures and safety standards compliance. Environmental labs use pH meters to test soil, wastewater and drinking water, keeping them on track with health regulations. The pH meter is essential to the lab as it adds to the accuracy, trust and consistency of measurements, and further is is an essential component necessary for research, industry or QC.
Q1: In drinking water, what is the acceptable pH range?
Ans: Drinking water is considered safe and satisfactory between the pH of 6.5 to 8.5 according to BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards).
Q2: Why is the temperature compensation necessary in a pH meter?
Ans: pH is temperature dependent. A temperature sensor embedded in the pH meter compensates for reading errors caused by changes in solution temperature.
Q3: Can the pH of solids and semi–solids be measured using a pH meter?
Ans: Yes, there are special flat-surface or spear-tip electrodes designed to take pH measurements in emulsions, gels, meat and semi-solid food.
Q4: How frequently should a pH meter be calibrated?
Ans: A pH meter should preferably be calibrated for every use, when high accuracy is needed. For general use once daily, once weekly.
Presto Stantest is a top company in Asia that makes testing tools. Many industries trust Presto for giving good-quality pH meters and other testing machines. The company has more than 40 years of experience and is known for making strong, accurate, and easy-to-use products. Presto also follows international rules to make sure their tools work well. People choose PrestoGroup because of their very helpful team, quick service, and fair prices. Whether you are testing water, food, or chemicals, Presto has the right tools for your needs.
A pH meter is a precise, reliable, and essential tool for anyone who works with chemical solutions, water, or food products. Understanding its working principle, components, and proper handling procedures is key to ensuring accurate results.
Need help? Our team is just a phone call away.
Whether you're a lab technician, farmer, food manufacturer, or water treatment engineer, choosing the right type of pH meter and maintaining it well will yield long-term benefits.
Call : +91 9210 903 903
Email : info@prestogroup.com
What are ASTM standards, and why are they important in testing?
What is the difference between bursting strength and tensile strength?
What is a BCT calculator, and how is it used in box testing?
What does a GSM calculator measure?
What is the working principle of a spectrophotometer?
How is a moisture meter used to measure moisture in paper and cardboard?